
Order fulfillment is essential to a brand’s reputation, profitability, and customer retention. It serves as the backbone of any retail operation—without effective order fulfillment, sales diminish, jeopardizing the business’s viability.
Understanding Order Fulfillment: The Process Unveiled
The order fulfillment cycle consists of five primary steps, all of which culminate in the shipping of products to customers. This process takes place in one or more distribution centers and encompasses various activities, including inventory management, supply chain coordination, order processing, quality control, and customer support for issues such as returns or exchanges
The Five Steps of Order Fulfillment
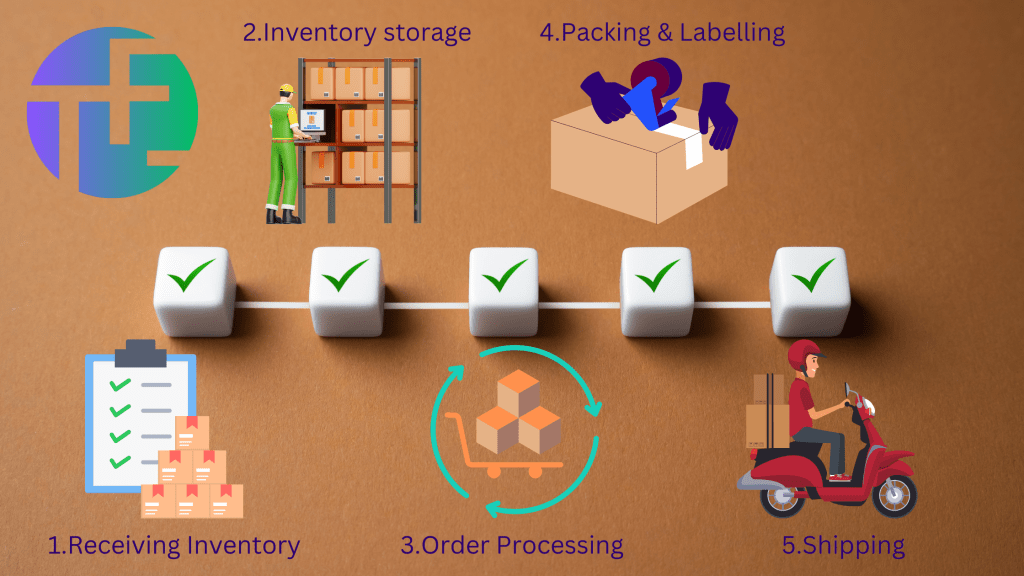
1. Receiving Inventory:
Inventory can arrive from various sources, including third-party suppliers, other company departments, or company-owned warehouses. Upon arrival, goods must be counted, inspected, and documented to confirm accurate quantities and acceptable quality. This process often employs SKUs or barcodes for efficient tracking and storage.
2. Inventory Storage:
After receiving inventory, products are recorded and either immediately distributed or placed into short- or long-term storage. The goal is to store items only as long as necessary to facilitate timely distribution for current sales, rather than holding excess stock for future sales.
3. Order Processing:
The order processing system governs the picking and packing activities for each customer order. This management system ensures that orders are efficiently handled according to predefined protocols.
4. Sorting:
Sorting consists of the picking and packing phases. A designated picking team gathers items based on the details specified in a packing slip, which includes item SKUs, colors, sizes, quantities, and specific locations in the warehouse. The packing team then chooses appropriate materials to minimize dimensional weight, calculated by the formula: length x width x height. Optimizing dimensional weight is crucial for reducing shipping costs and ensuring efficient transport, particularly given the limited space on delivery trucks.
5. Shipping:
The final step involves sending the order through a transportation channel or shipping node to reach the customer. Shipping costs are calculated based on whether the actual package weight or the dimensional weight is greater. Even lightweight items may incur additional costs if packed inefficiently. Carriers may have specific packaging requirements that, if not met, could lead to shipment delays. Additionally, shipping routes often employ multiple carriers to handle logistics, particularly when delivering to remote areas.
By understanding and optimizing each of these steps in the order fulfillment process, businesses can enhance efficiency, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, their bottom line.
Returns Processing
Returns processing begins by including shipping materials and a return label with the original order sent to customers. When a customer returns a product for either exchange or refund, it is essential to execute the process carefully to determine if the item can be restocked. Items that are malfunctioning or soiled cannot be restocked. The returns processing procedure includes quality control checks and sorting the returned products accordingly. Returned items are then either restocked for resale, returned to the vendor or manufacturer for a refund or credit, or sent to a recycling center.
Types of Order Fulfillment
There are four primary models for order fulfillment, each designed to meet specific business needs:
1. In-house Fulfillment: This model involves handling all steps of order fulfillment internally within the company.
2. Third-party Fulfillment: In this model, all order fulfillment activities are outsourced to a third-party vendor, allowing businesses to focus on other key areas.
3. Drop Shipping: This fulfillment method allows merchants to ship products from the manufacturer directly to customers.
4. Hybrid Fulfillment: The hybrid model combines two or more of the previous models. For instance, a company may choose to manage fulfillment for popular products internally while outsourcing fulfillment during peak periods, such as holidays, and employing drop shipping for larger items directly from the manufacturer.
Each of these order fulfillment models has its own set of benefits and challenges, allowing businesses to select the approach that best aligns with their operational goals.
Choosing an Order Fulfillment Strategy

When determining an order fulfillment strategy, businesses must evaluate their options based on available skills and resources.
- Companies with sufficient in-house capabilities may advantageously manage fulfillment processes internally, allowing for greater control over operations and costs.
- If a company lacks the necessary fulfillment and logistics expertise, it may be better to outsource these tasks entirely. Outsourcing enables the organization to concentrate on product development and sales, often leading to improved predictability.
- Drop-shipping reduces overhead costs and removes the middleman, which can lead to savings for buyers. However, it may limit the merchant’s control over inventory management and order fulfillment. Additionally, shipments may be delayed, as manufacturers are often located in different countries, which can increase shipping costs and times.
- For businesses with limited resources, a hybrid model can provide a balance between internal and outsourced fulfillment benefits.
While internal fulfillment requires managing staff, warehouse operations, and ensuring order accuracy, outsourcing can alleviate many of these burdens.
Order Fulfillment Challenges
Order fulfillment encompasses a variety of challenges that businesses frequently encounter, including supply shortages, inventory management issues, difficulties in demand forecasting, logistics planning complications, and disruptions within the supply chain.
- Inventory Management
A common challenge in order fulfillment is maintaining sufficient inventory levels. Running out of stock can lead to customer dissatisfaction, negatively impact the overall customer experience, and damage brand reputation. Once customer trust is compromised, it can be challenging to restore. However, customers may show increased understanding if stock shortages are due to factors like widespread weather events or natural disasters.
- Demand Planning
Conversely, overstocking can present its own set of problems, such as increasing storage and carrying costs. Excess inventory can also pose risks if demand for those items wanes before they are sold. Therefore, accurate demand forecasting and planning are crucial to ensure that inventory levels are maintained effectively — avoiding both stock-outs and excess stock.
- Logistics Planning
Logistics plays a vital role in customer satisfaction. Issues such as slow or missing deliveries, damaged items, and poor packaging can adversely affect a company’s reputation and future sales, ultimately impacting profitability. Thus, it is essential to manage logistics carefully to prevent shipping errors and item damage.
- Supply Chain Execution
An effective supply chain strategy involves evaluating the cost-benefit tradeoffs of operational decisions. For instance, choosing a sole supplier for a particular product may offer price breaks due to higher purchase volumes and can enhance the company’s priority status with the vendor. However, relying on a single supplier can be risky; any disruptions faced by that vendor, such as labor or supply shortages, can directly impact your business operations.
Conclusion
To make an informed decision about order fulfillment strategy, businesses should assess their product characteristics, available fulfillment options, and associated costs and challenges. Conducting a thorough financial analysis can help identify the most suitable approach for fulfilling orders effectively.


Leave a comment